What is the name designated to the group 1 elements? What does their electron dot diagram look like?

Sodium is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metallic. Sodium is an brine metallic, being in group 1 of the periodic table, because it has a unmarried electron in its outer shell that it readily donates, creating a positively charged atom—the Na+ cation.
Summary
| Element | Sodium |
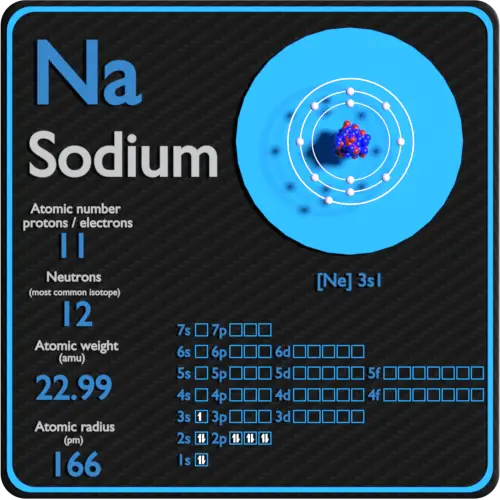
| Atomic number | 11 |
| Diminutive mass [amu] | 22.9897 |
| Diminutive mass [pm] | 166 |
| Density at STP [g/cm3] | 0.968 |
| Number of protons | 11 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 23 |
| Number of electrons | 11 |
| Electron configuration | [Ne] 3s1 |
| Oxidation states | -1; +1 |
| Electron affinity [kJ/mol] | 52.8 |
| Electronegativity [Pauling scale] | 0.93 |
| Get-go ionization energy [eV] | 5.1391 |
Atomic Number – Protons, Electrons and Neutrons in Sodium
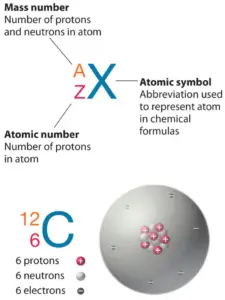 Sodium is a chemic element with atomic number11 which means there are 11 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electric charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to1,602 ten x-19 coulombs.
Sodium is a chemic element with atomic number11 which means there are 11 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called theatomic number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The total electric charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to1,602 ten x-19 coulombs.
The full number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is chosen theneutron number of the cantlet and is given thesymbol North. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number:N+Z=A. The departure between the neutron number and the diminutive number is known as theneutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, in that location is usually a diverseness of stable isotopes.Isotopes are nuclides that have the same diminutive number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes ofSodium are23.
Diminutive Mass of Sodium
Diminutive mass ofSodium is22.9897 u.
The diminutive mass is the mass of an atom. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a unmarried particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. The diminutive mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about ten-12of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the cantlet. Note that, each element may comprise more isotopes, therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occuring isotopes and their abundance.
Atomic Radius of Sodium
The atomic radius ofSodiumatom is 166pm (covalent radius).
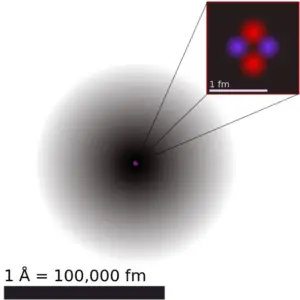
Information technology must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron deject extends from the nucleus. However, this assumes the cantlet to showroom a spherical shape, which is just obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. Therefore, in that location are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius.
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom ofSodiumis11. Each electron is influenced past the electrical fields produced past the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the cantlet.
Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemic behavior of atoms, theatomic number identifies the various chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of breakthrough mechanics. The number of electrons in each chemical element's electron shells, particularly the outermost valence trounce, is the chief factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing diminutive number Z.
Electron configuration ofSodiumis[Ne] 3s1.
Possible oxidation states are-1; +1.
Density of Sodium
Density ofSodiumis0.968g/cm3 .
Typical densities of various substances are at atmospheric force per unit area.
Density is defined as themass per unit book. Information technology is anintensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume:
ρ = g/V
Atomic Masses of Elements
Atomic Radii of Elements
Densities of Elements

Electron Affinity – Sodium
Electron affinity ofSodium is52.eight kJ/mol.
In chemistry and diminutive physics, theelectron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as:
the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral cantlet or molecule (in the gaseous stage) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion.
X + e– → Ten– + free energy Affinity = – ∆H
In other words, information technology can exist expressed as the neutral atom'slikelihood of gaining an electron. Note that, ionization energies mensurate the tendency of a neutral cantlet to resist the loss of electrons. Electron affinities are more than difficult to measure out than ionization energies.
Electronegativity of Sodium
Electronegativity ofSodium is0.93.
Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical holding that describes the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards this atom. For this purposes, adimensionless quantity thePauling scale, symbol χ, is the most commonly used.
The electronegativity of Sodium is: χ = 0.93
First Ionization Energy of Sodium
First Ionization Energy of Sodium is 5.1391 eV.
Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom.
X + energy → X+ + e−
where 10 is any atom or molecule capable of existence ionized, X+ is that atom or molecule with an electron removed (positive ion), and eastward− is the removed electron.
A Sodium atom, for example, requires the following ionization energy to remove the outermost electron.
Na + IE → Na+ + e− IE = 5.1391 eV
Electronegativity of Elements
Ionization Energy of Elements

Source: www.luciteria.com
Other properties of Sodium
Source: https://material-properties.org/Sodium-periodic-table-atomic-number-mass-radius-density/
0 Response to "What is the name designated to the group 1 elements? What does their electron dot diagram look like?"
Postar um comentário